Understanding Powertrain Technologies Today
The powertrain is a fundamental component of any vehicle, responsible for generating and delivering power to the wheels. It encompasses the engine, transmission, driveshaft, differentials, and axles, all working in concert to propel a vehicle forward. Modern automotive engineering has seen significant advancements in powertrain design, moving beyond conventional internal combustion engines to embrace a diverse range of electric and hybrid solutions. These innovations are reshaping the landscape of mobility, influencing everything from fuel efficiency and environmental impact to vehicle performance and the overall driving experience on the road.
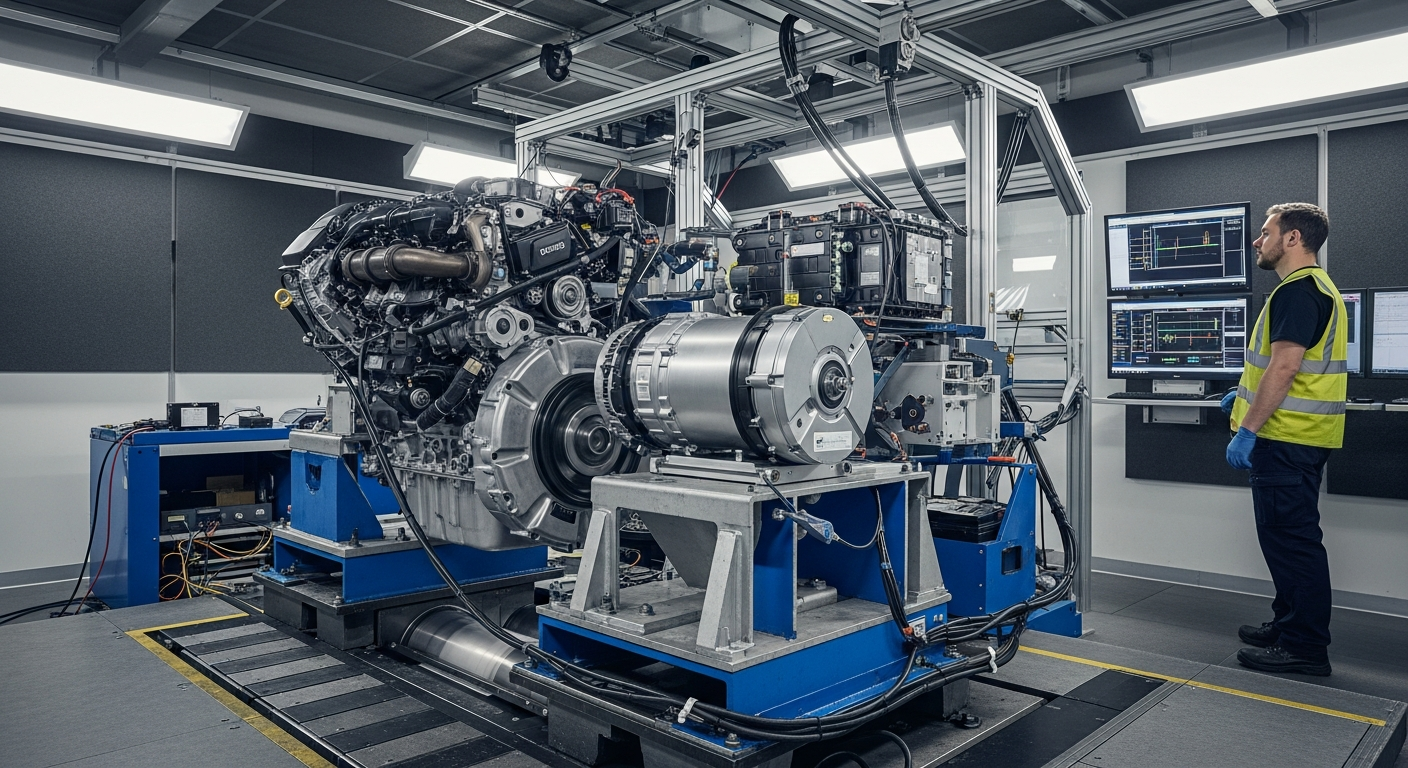
What Defines a Vehicle Powertrain?
The powertrain essentially represents the heart of a vehicle’s propulsion system. It begins with the power source, traditionally an internal combustion engine, but increasingly includes electric motors and battery packs. This power is then managed and transmitted through a series of components, including the transmission (gearbox), driveshaft, differentials, and ultimately to the wheels. The primary function of the powertrain is to convert the energy generated by the power source into kinetic energy, enabling the vehicle’s movement. Its design significantly impacts a vehicle’s overall performance, fuel consumption, and its interaction with the road, playing a crucial role in modern transport.
Advancements in Internal Combustion Engine Technology
While electric and hybrid technologies gain prominence, internal combustion engine (ICE) innovation continues. Engineers focus on enhancing efficiency and reducing emissions through various methods. Technologies like direct fuel injection, variable valve timing, turbocharging, and cylinder deactivation optimize fuel combustion and power output. Advanced engine designs utilize lighter materials and improved aerodynamics to reduce overall vehicle weight and drag, further contributing to better fuel economy. These continuous improvements ensure that ICEs remain a viable and evolving part of the global mobility landscape, even as the industry transitions towards more sustainable alternatives.
Exploring Electric and Hybrid Powertrain Systems
The shift towards electric and hybrid powertrains marks a significant evolution in automotive technology. Electric vehicles (EVs) rely entirely on electric motors powered by rechargeable battery packs, offering zero tailpipe emissions and instantaneous torque for smooth driving. Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) combine an internal combustion engine with one or more electric motors and a battery. There are various hybrid configurations, including parallel, series, and plug-in hybrids (PHEVs), each offering different balances of electric range, fuel efficiency, and performance. This diversification in powertrain options provides consumers with choices that align with different driving needs and sustainability goals, driving innovation in transport.
Powertrain Influence on Driving Dynamics and Safety
The choice of powertrain technology has a profound impact on a vehicle’s driving dynamics and safety characteristics. Electric powertrains, for instance, often allow for a lower center of gravity due to battery placement, enhancing stability and handling. The immediate torque delivery of electric motors provides swift acceleration, which can be beneficial for merging into traffic. Advanced electronic control systems, often integrated with the powertrain, contribute to enhanced safety features like traction control and stability control. These systems work to manage power delivery to the wheels, improving grip and control on various road conditions, thereby elevating the overall driving experience and occupant safety.
Future Directions in Powertrain Innovation
The future of powertrain technology is characterized by a relentless pursuit of innovation, focusing on greater efficiency, sustainability, and integration with emerging technologies. Research into advanced battery chemistries, hydrogen fuel cells, and alternative fuels continues to push the boundaries of what is possible. The development of autonomous driving systems also profoundly influences powertrain design, requiring seamless integration of power delivery with sophisticated sensor arrays and artificial intelligence. Materials science plays a critical role in creating lighter, stronger components, while advancements in connectivity enable vehicles to optimize their performance based on real-time traffic and environmental data. These efforts collectively aim to create a more sustainable and intelligent transport ecosystem for the future.
Real-World Powertrain Examples and Specifications
Understanding the practical application of these technologies can be useful. Here is a general comparison of common powertrain types found in vehicles today, highlighting their core characteristics and estimated operational costs. These examples illustrate the diverse approaches manufacturers take to achieve performance and efficiency.
| Product/Service | Provider | Cost Estimation (Fuel/Electricity) |
|---|---|---|
| Conventional ICE (Gas) | Toyota Corolla | Moderate (varies by fuel price) |
| Hybrid Electric (HEV) | Honda Civic Hybrid | Lower than ICE (less fuel usage) |
| Plug-in Hybrid (PHEV) | Hyundai Ioniq PHEV | Varies (depends on electric usage) |
| Battery Electric (EV) | Tesla Model 3 | Low (varies by electricity rates) |
| Fuel Cell Electric | Toyota Mirai | Moderate (depends on hydrogen cost) |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
The evolution of powertrain technologies reflects a dynamic industry responding to demands for improved efficiency, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced driving experiences. From the ongoing refinement of internal combustion engines to the rapid advancement of electric and hybrid systems, the core goal remains to provide effective and sustainable mobility solutions. As innovation continues, future powertrains are expected to be even more integrated, efficient, and responsive to the needs of a changing world, shaping the future of transport and driving on our roads.






